Introduction
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are a key element of industrial infrastructure, enabling monitoring, control, and data collection from processes occurring in various facilities. In recent years, we have observed a significant transformation of these systems, driven by new technologies, growing operational requirements, and changing market conditions.
In this article, we present the most significant trends in SCADA system development that will shape the industry in 2025. Particular attention is paid to solutions dedicated to water infrastructure, which can bring breakthrough benefits in water resource management.
According to the "Global SCADA Market Outlook 2024" report, the value of the global SCADA systems market will increase by 7.8% in 2024, reaching $14.3 billion. The main driver of this growth will be new implementations in the water and energy sectors.
Key Trends for 2025
1. Cloud-based SCADA
One of the most dynamically developing trends is the migration of SCADA systems to cloud environments. Cloud solutions offer a range of benefits that are particularly important in the context of managing distributed infrastructure:
- Access to data and control from any location and device
- Flexible scaling of resources according to needs
- Lower IT infrastructure costs and easier system expansion
- Automatic updates and easier implementation of new features
In 2024, we anticipate a significant increase in hybrid implementations, combining local SCADA systems with cloud solutions. Such architecture allows critical control functions to be maintained locally while taking advantage of cloud benefits for analytical functions and reporting.
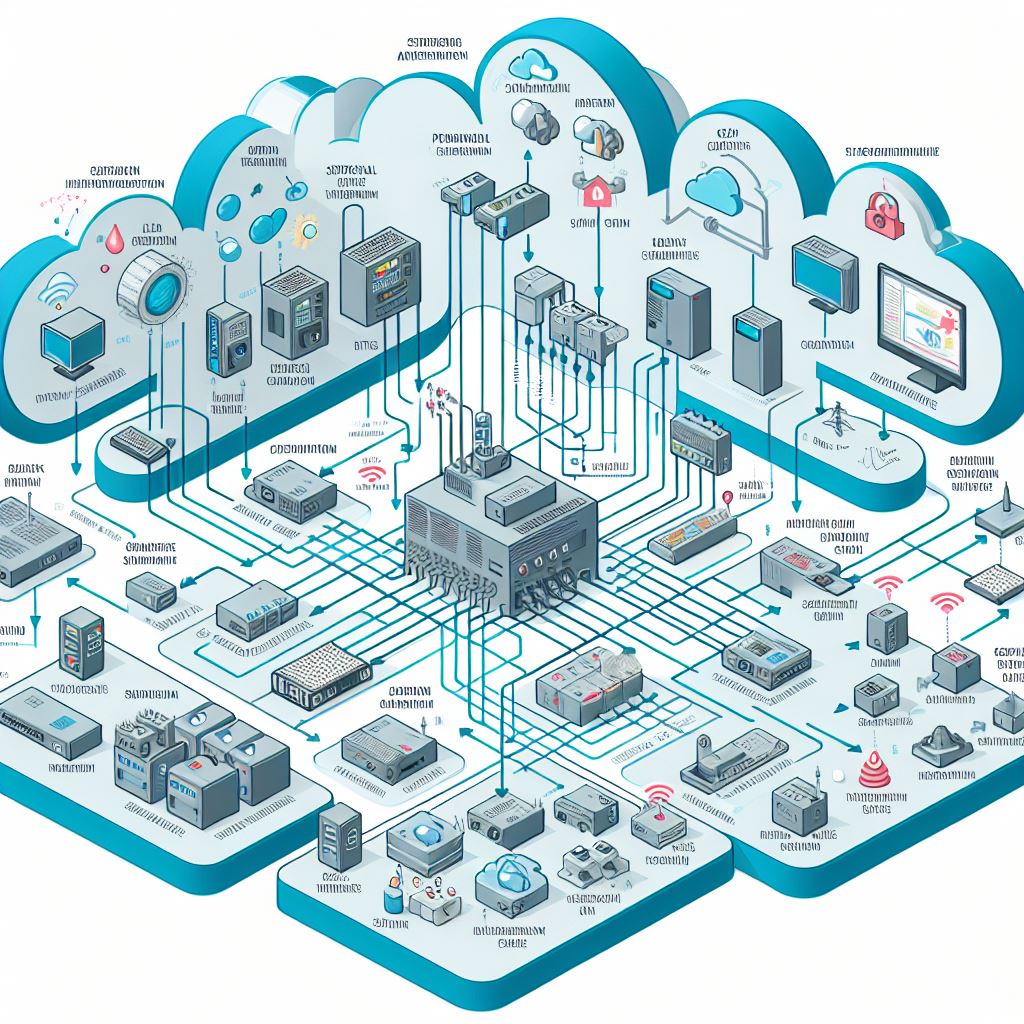
Diagram: Hybrid SCADA architecture model with local and cloud elements
2. IoT Integration with SCADA Systems
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the way we collect and analyze data. In 2024, we will see even deeper integration of IoT devices with SCADA systems, particularly in the context of water utilities:
- Mass deployments of intelligent wireless sensors
- Real-time monitoring of water quality parameters
- Leak detection and anomalies in the water supply network
- Energy consumption optimization in pumping stations
The key to effective IoT integration with SCADA systems will be the standardization of communication protocols and the development of platforms connecting data from various sources into a coherent information ecosystem.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are technologies that will change how SCADA systems process and utilize data in 2024. The main areas of application include:
- Predictive maintenance of water infrastructure
- Real-time process optimization
- Anomaly detection and potential threat identification
- Advanced historical data analytics
Next-generation SCADA systems, such as HydroNexis, will be able not only to collect data but also to independently interpret it and make autonomous decisions based on advanced AI models.
4. Mobile-first and User-Oriented Interfaces
User expectations regarding SCADA systems are evolving. In 2024, the standard will include:
- Intuitive interfaces accessible on mobile devices
- Advanced data visualizations and dashboards
- Personalization of views and reports
- Voice interfaces and chatbots for system interaction
SCADA system design will increasingly focus on user experience (UX), simplifying complex operations and presenting data in a way that facilitates decision-making.
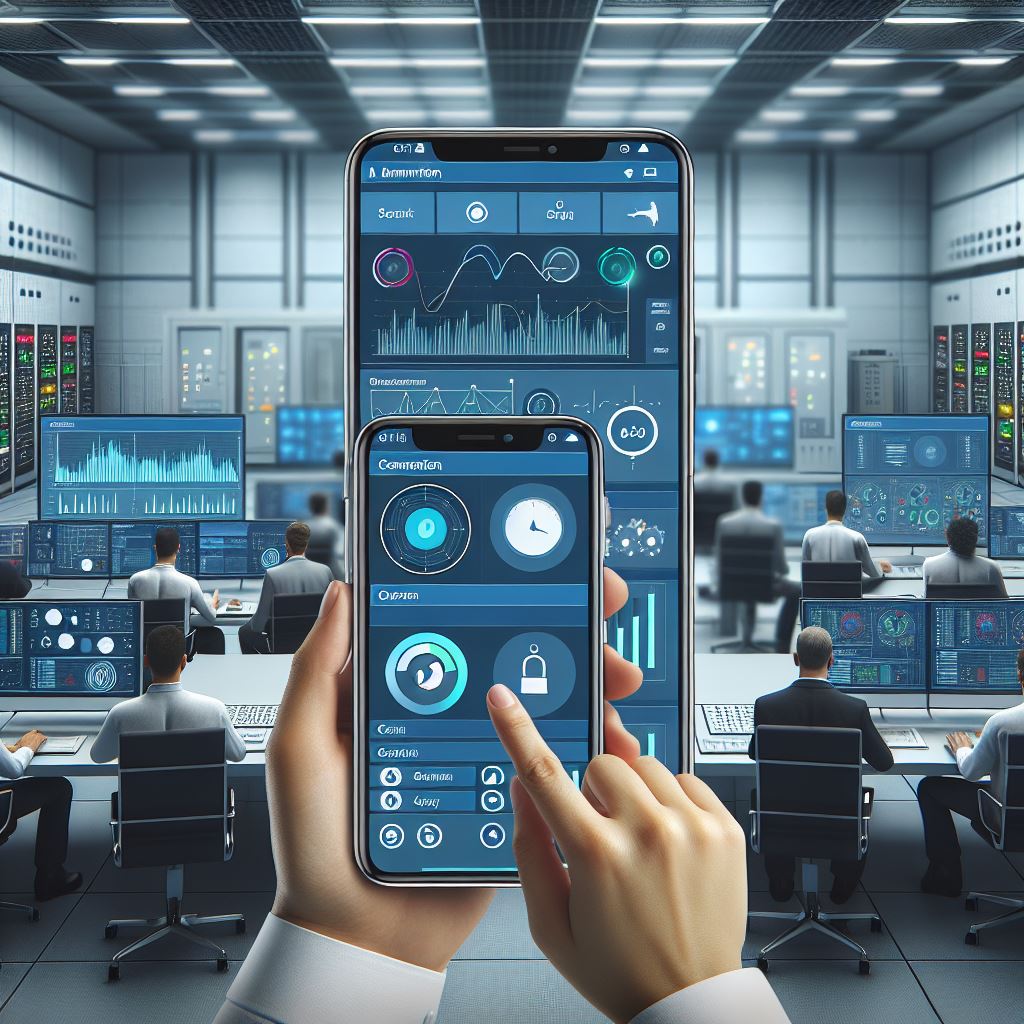

Example of a responsive SCADA system interface accessible on various devices
5. Cybersecurity as a Priority
With the increasing number of cyberattacks on critical infrastructure, SCADA system security is becoming an absolute priority. In 2024, the standard will include:
- Multi-layered security architecture
- Advanced cryptographic techniques
- Real-time security monitoring
- Automated incident detection and response
- Regular security audits and penetration testing
Leading SCADA system providers, including HydroNexis, are implementing a "security by design" approach, where security is an integral part of system architecture rather than an add-on implemented after the fact.
6. Augmented Reality (AR) in Infrastructure Maintenance
AR (Augmented Reality) technologies open new possibilities in the maintenance and servicing of water infrastructure. In 2024, we expect the popularization of:
- AR applications supporting field technicians
- Real-time SCADA data display on physical objects
- Remote expert assistance using AR
- Training using immersive technologies
AR technologies will enable faster problem diagnosis, error reduction, and more efficient use of technical expertise.
Case Study: Digital Water Works
American company Digital Water Works implemented a pioneering cloud-based SCADA platform with IoT technologies in three large water utilities. The system integrates:
- Over 15,000 intelligent sensors distributed throughout the infrastructure
- Advanced AI models for water consumption prediction and leak detection
- Mobile interfaces for field personnel
- AR solutions supporting repairs and maintenance
One year after system implementation, the following results were achieved:
- 23% reduction in water losses through faster leak detection
- 18% decrease in energy consumption through intelligent pump control
- 35% reduction in response time to failures
- Increased infrastructure lifespan through predictive maintenance
Challenges and Obstacles
Despite promising prospects, the implementation of modern SCADA systems faces several challenges:
- Initial costs - modernizing existing systems involves significant financial outlays.
- Staff competencies - new technologies require new skills and organizational change.
- Integration with existing systems - connecting legacy systems with new technologies often presents technical challenges.
- Data security - greater data availability is associated with higher cybersecurity risks.
- Standardization - lack of uniform standards complicates the integration of different systems and devices.
Summary
SCADA systems are undergoing a fundamental transformation, evolving from closed, isolated control systems into open, intelligent platforms integrating various technologies. The year 2024 will bring further acceleration of this evolution, particularly in the areas of cloud computing, IoT, artificial intelligence, and mobility.
Water utilities that decide on early adoption of these technologies can gain significant operational advantages, reducing costs, increasing efficiency, and improving service quality. The key to success will be a strategic approach to digital transformation, considering both technological and organizational aspects.



Comments (12)
John Smith
September 30, 2023, 09:15
Very interesting article! As someone who has been working in the water industry for 15 years, I see huge potential in integrating IoT with SCADA systems. In our utility, we have already started testing intelligent sensors for water quality monitoring and leak detection.
Margaret Wilson
September 29, 2023, 16:42
Can you recommend any proven cloud solutions for small water utilities? Our current SCADA system needs modernization, but we have limited IT budget and resources.
Anna Smith Author
September 29, 2023, 18:30
I recommend SCADAaaS (SCADA as a Service) solutions for smaller utilities. Companies like WaterCloud or AquaEdge offer subscription models with low initial costs. I'm happy to discuss this in detail - please contact me through LinkedIn.
Peter Adams
September 29, 2023, 11:23
Excellent overview of trends! I was particularly interested in the AR section for infrastructure maintenance. Do you have information about specific implementations of this technology in the US? What about the regulatory framework in this area?
Alice Brown
September 28, 2023, 22:05
I missed a discussion of data privacy and GDPR compliance in the article. With such large amounts of collected information, proper personal data management becomes a key challenge, especially in the context of cloud integration.
Thomas Crawford
September 28, 2023, 15:47
From my experience as an IT specialist in a water utility, the biggest challenge in implementing modern SCADA systems is integration with older, existing systems. Sometimes the cost of this integration exceeds the benefits of the new technology.
Add a Comment